The world of web development is exciting, lucrative, and growing fast. But if you are just starting out, it can also feel incredibly overwhelming.
Should you learn React first? What is a bundler? How much CSS do you actually need to know?
If you’ve ever felt lost in the sea of tutorials, you’re not alone. The secret to success isn’t trying to learn everything; it’s learning the right things in the right order.
Based on current industry demands, we’ve put together a practical, no-nonsense roadmap to take you from writing your first line of HTML to landing your first job as a Frontend Developer.
Let’s break down the journey.
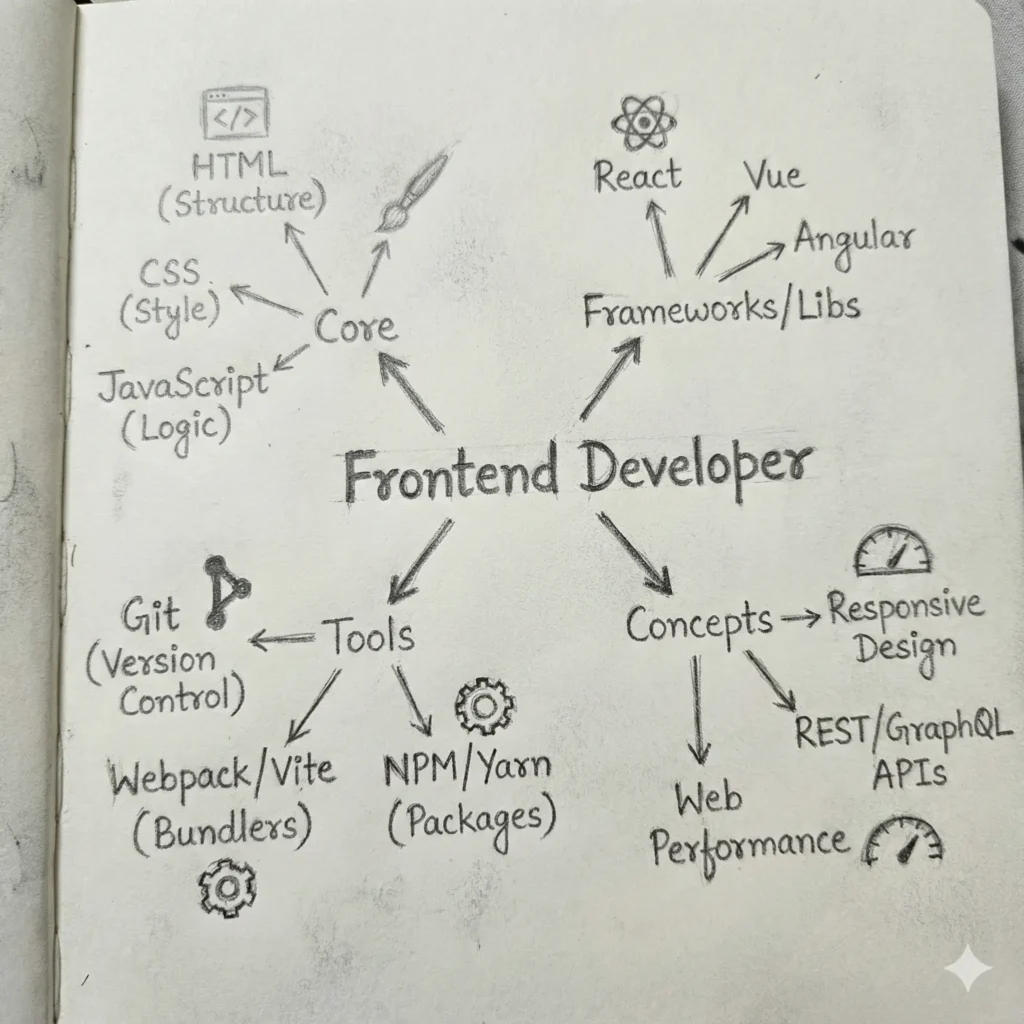
The Visual Guide
Before diving into the steps, visualize the landscape. This mind map outlines the ecosystem you are about to enter. Keep this mental model handy—it helps connect the dots between the tools you’ll be learning.
Step 1: The Unshakeable Foundations (HTML & CSS)
You cannot build a skyscraper on quicksand. Before touching any complex logic, you must master the building blocks of the web.
- HTML5: Learn semantic structure. Don’t just use
<div>for everything; understand when to use<header>,<nav>,<article>, and<button>. Accessibility starts here. - Modern CSS: Forget floating elements. Master Flexbox and CSS Grid. These are essential for laying out modern interfaces. Understand responsiveness—how to make a site look good on a phone versus a 4K monitor using media queries.
Pro Tip: Don’t rush this. Build several static landing pages. Try to clone the layout of your favorite website using only HTML and CSS.
Step 2: Core JavaScript (The “Magic”)
This is where your websites come alive. JavaScript is the logic that makes buttons do things, fetches data, and updates the page without reloading.
- The Basics: Get comfortable with variables, data types, loops, and functions.
- DOM Manipulation: Learn how to use JavaScript to select HTML elements on your page and change their content or style dynamically.
- ES6+ Concepts: Modern JavaScript looks different than it did ten years ago. Get familiar with arrow functions, destructuring, and array methods like
.map()and.filter().
Warning: Many beginners jump straight to frameworks like React here. Do not do this. If you don’t understand vanilla JavaScript, frameworks will feel confusing and frustrating.
Step 3: Essential Tools of the Trade (Git & NPM)
Modern development doesn’t happen in a vacuum. You need tools to manage your code and use other people’s code.
- Version Control (Git & GitHub): Git is an “undo” button for your entire project history. GitHub is where you show off your code to employers. Learn the basics of committing, pushing, and branching.
- Package Managers (NPM): You rarely write everything from scratch. NPM (Node Package Manager) allows you to install external libraries (like date pickers or icon sets) into your project.
Step 4: Advanced Frontend Concepts & APIs
This is the biggest hurdle for most self-taught developers, and it’s usually the difference between a hobbyist and a hireable junior dev.
Most modern web apps work by fetching data from a backend server (an API) and displaying it.
- Asynchronous JavaScript: Understand the event loop. Master Promises and the modern async/await syntax to handle operations that take time (like loading data) without freezing the user interface.
- Fetching APIs: Learn how to use
fetch()to get JSON data from a public API (like a weather service or movie database) and render that data onto your page. - Error Handling: What happens when the API is down? Learn to handle errors gracefully so your app doesn’t just crash with a white screen.
Step 5: Picking a Framework (Focus on React)
Once your vanilla JavaScript is solid, a framework helps you build complex, interactive applications faster and more efficiently.
While Vue and Angular are great, React currently holds the largest market share for job openings.
- React Core: Learn about Components, Props, and State.
- Hooks: Master
useStateanduseEffect. These are the bread and butter of modern React development.
Step 6: The Real World: Projects & Portfolio
You cannot learn to swim by reading a book about swimming. You have to get in the water. Tutorials are great, but you need to build things without a guide holding your hand.
employers don’t care about the tutorials you watched; they care about what you can build.
Build these three projects in order:
- The Portfolio Website: A static site built with HTML/CSS (and maybe a little JS) to showcase who you are.
- The Dashboard/App: An app that fetches data from a public API. For example, a “Crypto Price Tracker” or a “Recipe Finder” app using React. This proves you understand asynchronous data.
- The E-Commerce UI: A complex UI with a shopping cart state. This proves you can manage complex state across different parts of an application.
Final Thoughts: The Journey is Continuous
This roadmap gets you to “job-ready,” but the learning never stops. Technology evolves rapidly. The key trait of a successful developer isn’t memorizing syntax, but having the curiosity and persistence to figure things out.
Start today. Write code every day, even if it’s just for 20 minutes. Consistency beats intensity. Good luck on your journey!